プライベートIPアドレスはインターネットとIPレベルで接続しない限り自由に使用できるアドレスのことで
|
しかしこの方法の不便なところは、
今回はFreeBSDで動作するnatdを紹介します。NATではグローバルIPアドレスとプライベートIPアドレスは1対1変換のため同時に複数の接続はできないと言われていますが、natdはPacket Aliasingというしくみで、1つのグローバルIPアドレスで複数の同時接続を可能にしています(IP Masqueradeも同時接続可能です)。

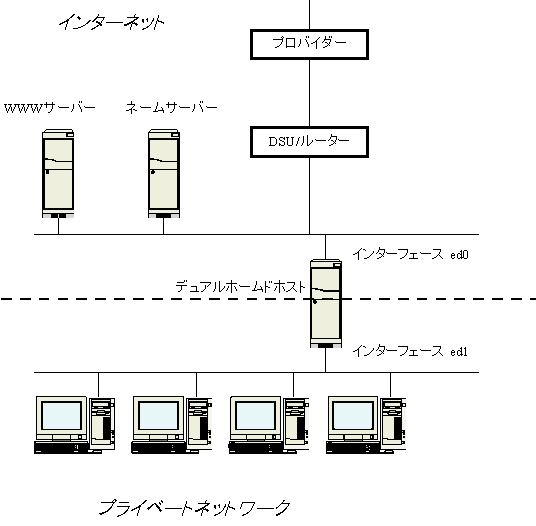
natdを動かすマシンのネットワーク環境は次のようにします。
|
# # Configuration file for natd. # # # Logging to /var/log # log no # # Incoming connections. # deny_incoming yes # # Use sockets to avoid port clashes. # use_sockets no # # Avoid port changes if possible. Makes rlogin work # in most cases. # same_ports yes # # Verbose mode. Enables dumping of packets and disables # forking to background. # verbose no # # Divert port. Can be a name in /etc/services or numeric value. # port 6668 # # Interface name or address being aliased. Either one, # not both is required. # # alias_address xxx.xxx.xxx.aaa interface ed0 # # Alias unregistered addresses or all addresses. # unregistered_only yes # # Configure permanent links. If you use host names instead # of addresses here, be sure that name server works BEFORE # natd is up - this is usually not the case. So either use # numeric addresses or hosts that are in /etc/hosts. # # Map connections coming to port 30000 to telnet in my_private_host. # Remember to allow the connection /etc/rc.firewall also. #permanent_link tcp my_private_host:telnet 0.0.0.0:0 30000 # # Map connections coming from host.xyz.com to port 30001 to # telnet in another_host. #permanent_link tcp another_host:telnet host.xyz.com:0 30001 |
|
#!/bin/sh
#ipfwのルールのフラッシュ
#ed0から出入りするIPパケットをdivert port 6668に流す
#natdの起動
#ネットワークインターフェース間のIPパケットの転送を有効にする |